Assigning a value of one type to a variable of another type is known as Type Casting. If the data types are compatible, then Java will perform the conversion
automatically known as Automatic Type Conversion and if not then they
need to be casted or converted explicitly.
Example :
Example :
Example :
int x = 10;
byte y = (byte)x;- Widening Casting(Implicit)
- Narrowing Casting(Explicitly done)

Widening or Automatic type converion
Automatic Type casting take place when,- the two types are compatible
- the target type is larger than the source type
public class Test
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int i = 100;
long l = i; //no explicit type casting required
float f = l; //no explicit type casting required
System.out.println("Int value "+i);
System.out.println("Long value "+l);
System.out.println("Float value "+f);
}
} O/P :-
Int value 100
Long value 100
Float value 100.0
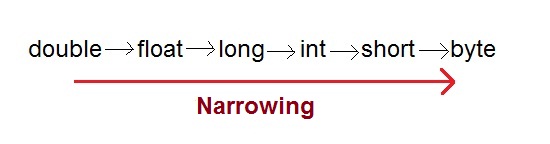
Narrowing or Explicit type conversion
When you are assigning a larger type value to a variable of smaller type, then you need to perform explicit type casting.Example :
public class Test
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double d = 100.04;
long l = (long)d; //explicit type casting required
int i = (int)l; //explicit type casting required
System.out.println("Double value "+d);
System.out.println("Long value "+l);
System.out.println("Int value "+i);
}
} O/P :
Double value 100.04
Long value 100
Int value 100
No comments:
Post a Comment